An estimated 576-740 million people in the world are infected with hookworm. Hookworm was once widespread in the United States, particularly in the southeastern region, but improvements in living conditions have greatly reduced hookworm infections. Hookworm, Ascaris, and whipworm are known as soil-transmitted helminths (parasitic worms). Together, they account for a major burden of disease worldwide.
Hookworms live in the small intestine. Hookworm eggs are passed in the feces of an infected person. If the infected person defecates outside (near bushes, in a garden, or field) of if the feces of an infected person are used as fertilizer, eggs are deposited on soil. They can then mature and hatch, releasing larvae (immature worms). The larvae mature into a form that can penetrate the skin of humans. Hookworm infection is mainly acquired by walking barefoot on contaminated soil. One kind of hookworm can also be transmitted through the ingestion of larvae.
Most people infected with hookworms have no symptoms. Some have gastrointestinal symptoms, especially persons who are infected for the first time. The most serious effects of hookworm infection are blood loss leading to anemia, in addition to protein loss. Hookworm infections are treatable with medication prescribed by your health care provider.
Hookworm is an intestinal parasite of humans. The larvae and adult worms live in the small intestine can cause intestinal disease. The two main species of hookworm infecting humans are Anclostoma duodenale and Necator americanus.
Hookworm eggs are passed in the feces of an infected person. If an infected person defecates outside (near bushes, in a garden, or field) or if the feces from an infected person are used as fertilizer, eggs are deposited on soil. They can then mature and hatch, releasing larvae (immature worms). The larvae mature into a form that can penetrate the skin of humans. Hookworm infection is transmitted primarily by walking barefoot on contaminated soil. One kind of hookworm (Anclostoma duodenale)can also be transmitted through the ingestion of larvae.
People living in areas with warm and moist climates and where sanitation and hygiene are poor are at risk for hookworm infection if they walk barefoot or in other ways allow their skin to have direct contact with contaminated soil. Soil is contaminated by an infected person defecating outside or when human feces ("night soil") are used as fertilizer. Children who play in contaminated soil may also be at risk.
Itching and a localized rash are often the first signs of infection. These symptoms occur when the larvae penetrate the skin. A person with a light infection may have no symptoms. A person with a heavy infection may experience abdominal pain, diarrhea, loss of appetite, weight loss, fatigue and anemia. The physical and cognitive growth of children can be affected.
Health care providers can diagnose hookworm by taking a stool sample and using a microscope to look for the presence of hookworm eggs.
Do not walk barefoot in areas where hookworm is common and where there may be fecal contamination of the soil. Avoid other skin-to-soil contact and avoid ingesting such soil. Fecal contamination occurs when people defecate outdoors or use human feces as fertilizer.
The infection of others can be prevented by not defecating outdoors or using human feces as fertilizer, and by effective sewage disposal systems.
Hookworm infections are generally treated for 1-3 days with medication prescribed by your health care provider. The drugs are effective and appear to have few side effects. Iron supplements may be prescribed if you have anemia.
In developing countries, groups at higher risk for soil-transmitted helminth infections (hookworm, Ascaris, and whipworm) are often treated without a prior stool examination. Treating in this way is called preventive treatment (or "preventive chemotherapy"). The high-risk groups identified by the World Health Organization are preschool and school-age children, women of childbearing age (including pregnant women in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters and lactating women) and adults in occupations where there is a high risk of heavy infections. School-age children are often treated through school-health programs and preschool children and pregnant women at visits to health clinics.
The soil-transmitted helminths (hookworm, Ascaris, and whipworm) and four other "neglected tropical diseases" (river blindness, lymphatic filariasis, schistosomiasis and trachoma) are sometimes treated through mass drug administrations. Since the drugs used are safe and inexpensive or donated, entire risk groups are offered preventive treatment. Mass drug administrations are conducted periodically (often annually), commonly with drug distributors who go door-to-door. Multiple neglected tropical diseases are often treated simultaneously using MDAs.
The geographic distributions of the hookworm species that are intestinal parasites in human, Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus, are worldwide in areas with warm, moist climates and are widely overlapping. Necator americanus was widespread in the Southeastern United States until the early 20th century.
The human hookworms include the nematode species, Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus.
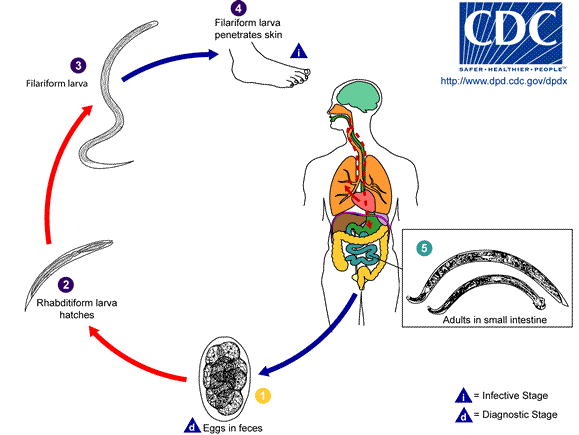
Eggs are passed in the stool, and under favorable conditions (moisture, warmth, shade), larvae hatch in 1 to 2 days. The released rhabditiform larvae grow in the feces and/or the soil, and after 5 to 10 days (and two molts) they become filariform (third-stage) larvae that are infective. These infective larvae can survive 3 to 4 weeks in favorable environmental conditions. On contact with the human host, the larvae penetrate the skin and are carried through the blood vessels to the heart and then to the lungs. They penetrate into the pulmonary alveoli, ascend the bronchial tree to the pharynx, and are swallowed. The larvae reach the small intestine, where they reside and mature into adults. Adult worms live in the lumen of the small intestine, where they attach to the intestinal wall with resultant blood loss by the host. Most adult worms are eliminated in 1 to 2 years, but the longevity may reach several years.
Some A. duodenale larvae, following penetration of the host skin, can become dormant (in the intestine or muscle). In addition, infection by A. duodenale may probably also occur by the oral and transmammary route. N. americanus, however, requires a transpulmonary migration phase.
Life cycle image and information courtesy.
High-intensity hookworm infections occur among both school-age children and adults, soil-transmitted helminthsAscaris and whipworm. High-intensity infections with these worms are less common among adults. The most serious effects of hookworm infection are the development of anemia and protein deficiency caused by blood loss at the site of the intestinal attachment of the adult worms. When children are continuously infected by many worms, the loss of iron and protein can retard growth and mental development.
The standard method for diagnosing the presence of hookworm is by identifying hookworm eggs in a stool sample using a microscope. Because eggs may be difficult to find in light infections, a concentration procedure is recommended.
The best way to avoid hookworm infection is not to walk barefoot in areas where hookworm is common and where there may be human fecal contamination of the soil. Also, avoid other skin contact with such soil and avoid ingesting it.
Infection can also be prevented by not defecating outdoors and by effective sewage disposal systems.
For more information view the source:Center for Disease Control
Recommended Test:Full GI Panel
Recommended Product:Freedom Cleanse Restore Parasite Cleanse